Front Line Doctors Ivermectin Protocol for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 (2025)
FLCCC (Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care) Protocols
All the component medicines are FDA-approved (except ivermectin), inexpensive, readily available and have been used for decades with well-established safety profiles.
PREVENTION PROTOCOL
- At the onset of any flu-like symptoms, please refer to the I-CARE Early COVID Treatment Protocol or I-CARE: RSV and Flu Treatment Protocols.
- Note that there are two I-Prevent Protocols; the I-Prevent Covid protocol to prevent Covid and the I-Prevent Post vaccine protocol to prevent vaccine injury.
The following protocol can be used for both pre-exposure and post-exposure prevention. Follow post-exposure prevention if a household member is COVID-positive or if you have had prolonged exposure to COVID but have not developed symptoms. (Last updated: December 2024)
- New evidence in use of Listerine for short term use only. (Dec 2024 update)
- Caution on potential tooth staining from mouthwash (Feb 2024 update)
How to prevent infection before you’ve been exposed (Pre-exposure)
- Antiseptic antimicrobial mouthwash: gargle twice daily (do not swallow). Choose mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine, povidone-iodine (Immune Mist™) or cetylpyridinium chloride (e.g., Scope, Act, Crest).
- Vitamin D: dosing varies; optimal target is greater than 50 ng/ml (Table 1) presents a safe and practical treatment schedule for raising serum concentrations in non-urgent situations. The dosing schedule illustrated in Table 2 should be used when recent serum concentration levels are unavailable. (Nutrients 2024)
- Vitamin C: 500 mg twice daily. (PaleoValley Essential C Complex)
- Zinc: 20-50 mg/day. (Life Extension Enhanced Zinc Lozenges) Commercial zinc supplements are commonly formulated as zinc oxide or salts with acetate, gluconate, and sulfate.
- Melatonin: 1-6 mg nightly (slow/extended)
- Begin with 1 mg and increase as tolerated to 6 mg at night. Causes drowsiness. Some patients are intolerant to melatonin, having very disturbing and vivid dreams; in these patients, it may be best to start with a 0.3 mg slow-release tablet and increase slowly, as tolerated.
- Elderberry syrup, supplements or gummies: follow manufacturer’s dosing recommendations
- Take during periods of high transmission of COVID-19, influenza, and RSV. A triple combination containing elderberry, Vitamin C, and zinc may be a convenient approach. Patients with autoimmune disease should take for 2 weeks or less and monitor their symptoms closely.
- Resveratrol or a Combination Flavonoid supplement: 400-500 mg daily.
- Coffee: One to two cups of caffeinated or decaffeinated coffee per day. (One Day MD)
- The safety of resveratrol, quercetin, and pterostilbene has not been determined in pregnancy and they should therefore be avoided. Due to the possible drug interaction between quercetin and ivermectin, these drugs should not be taken simultaneously (i.e., should be staggered morning and night).
- Ivermectin: In the current situation of abundant natural immunity along with the recent circulation of less severe and more highly transmissible variants, chronic weekly or twice weekly ivermectin prophylaxis is no longer applicable to most people. The following prophylaxis approaches with ivermectin can be considered and applied based on patient preference, comorbid status, immune status, and in discussion with their provider:
- Twice weekly ivermectin at 0.2mg/kg; can be considered in those with significant comorbidity and lack of natural immunity or immunosuppressive states or those with long COVID or post-vaccine syndrome who are not already on ivermectin as treatment
- Daily ivermectin just prior to and during periods of high possible exposure such as travel, weddings, conferences, etc.
- Immediate initiation of daily ivermectin at treatment doses (0.4mg/kg) upon first symptoms of a viral syndrome
Table 1. Guidance on Upfront Loading Dose Regimens to Replenish Vitamin D Stores in the Body
When serum vitamin D levels are available, the doses provided in this table can be used for the longer-term maintenance of serum 25(OH)D concentration above 50 ng/mL (125 nmol/L). The table provides the initial bolus dose, weekly dose, frequency, and the duration of administration of oral vitamin D in non-emergency situations, in a non-obese, 70 kg adult. *
* A suitable daily or weekly maintenance dose to be started after completing the loading-dose schedule. The dose should be adjusted for those who are overweight (higher) or underweight (lower).
** To convert ng/mL to nmol/L, multiply the amount in ng by 2.5; One µg = 40 IU.
$ Mentioned replacement doses can be taken as single, cumulative doses, two to three times a week spread out over a few weeks.
$$ From the day one of week two onwards.
# Estimated total Vitamin D dose needed to replenish the body stores (i.e., the deficit) is provided in the last column.
(Table adapted with permission from S.J. Wimalawansa)
Table 2. Vitamin D Dosing in the Absence of a Baseline Vitamin D Level
Longer-term maintenance schedules of oral vitamin D based on body weight to maintain the levels above 50 ng/mL (125 nmol/L) when the serum 25(OH)D concentrations are unknown.
# For those with chronic comorbid conditions, such as hypertension, diabetes, asthma, COPD, CKD, depression, and osteoporosis, and to reduce all-cause mortality, higher doses of vitamin D are needed. For them, one can use the doses that are recommended for persons with obesity (BMI, 30–39: the third row).
$ Those with multiple sclerosis, cancer, migraine headaches, and psoriasis, and those routinely taking medications such as anti-epileptic and anti-retroviral agents that significantly increase the catabolism of vitamin D should consider taking age-appropriate doses recommended for those with morbid obesity (BMI ≥ 40; the higher end of the daily doses in the fourth row).
(Table adapted with permission from S.J. Wimalawansa)
How to prevent infection if you have potentially been exposed (Post-exposure)
- Nasal Spray and Mouthwash: 2-3 times daily. The combination of nasal antiseptic sprays and oropharyngeal mouthwashes is strongly suggested. Choose a nasal spray with 1% povidone-iodine (for example Immune Mist™, CofixRX™ or Ionovo™) and mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine, povidone-iodine or cetylpyridinium chloride (e.g., Scope, Act, Crest).
- Elderberry: four times daily as per manufacturer’s directions for 1 week (gummy, supplement, or syrup)
- Vitamin C: 500-1000 mg four times daily for 1 week
- Elemental Zinc: 50-90 mg daily for 1 week
- Melatonin: 2-5 mg at night (slow/extended release)
- Resveratrol/Combination Flavonoid supplement: 500 mg twice daily
- A flavonoid combination containing resveratrol, quercetin and pterostilbene is recommended.
- Ivermectin: 0.4 mg/kg immediately, then repeat second dose in 24 hours;
- Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ): 200 mg twice a day for 5 days.
- Nitazoxanide: 500-600 mg twice daily for 5 days
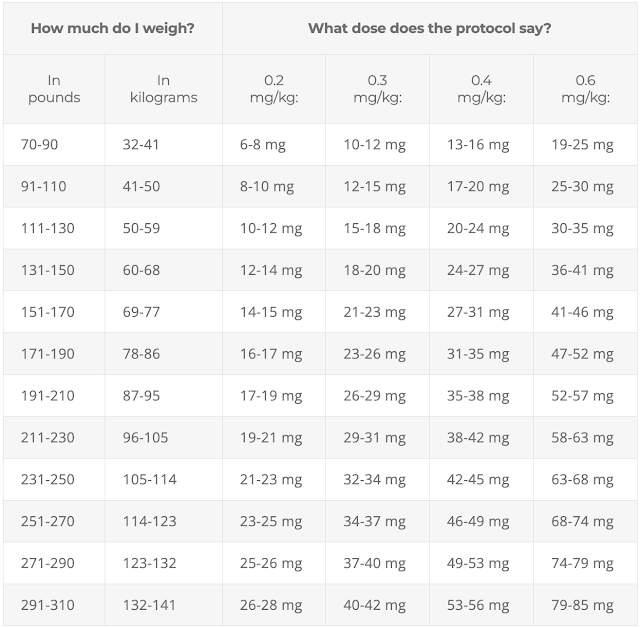
Table 3. How to calculate ivermectin dose
Note that ivermectin is available in different strengths (e.g., 3, 6 or 12 mg) and administration forms (tablets, capsules, drops, etc.). Note that tablets can be halved for more accurate dosing, while capsules cannot.EARLY TREATMENT PROTOCOL
Note that there are two I-Care Protocols; the I-Care Covid protocol (this article) to treat Covid and another protocol, I-Care Flu protocol; to treat influenza and RSV infections.
- The I-Care protocol has been updated and below is their latest version (December 2024).
- Short-term use of fluvoxamine to second line treatments was added with the April 2024 update.
First Line Therapies
(In order of priority; not all required)- Mouthwash: 3 times a day. Gargle three times a day (do not swallow) with an antiseptic-antimicrobial mouthwash containing chlorhexidine, cetylpyridinium chloride (e.g., Scope, Act, Crest), or 1% povidone-iodine (Immune Mist™).
- Nasal spray with 1% povidone-iodine (Immune Mist™): 2-3 times a day. Do not use for more than 5 days in pregnancy. If 1% product is not available, dilute the more widely available 10% solution (see box) and apply 4-5 drops to each nostril every 4 hours.
- Pour 1 ½ tablespoons (25 ml) of 10% povidone-iodine solution into a 250 ml nasal irrigation bottle.
- Fill bottle to top with distilled, sterile, or previously boiled water.
- To use: tilt head back, apply 4-5 drops to each nostril. Keep head tilted for a few minutes, then let drain.
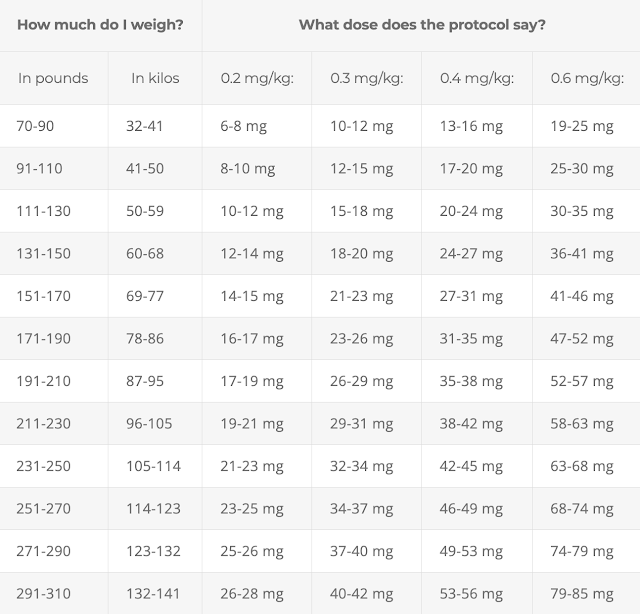
- Ivermectin: 0.4 to 0.6 mg/kg – one dose daily for at least 5 days or until symptoms resolve. If symptoms persist longer than 5 days, consult a healthcare provider. See Table 3 (above) for help with calculating correct dose. Due to a possible interaction between quercetin and ivermectin, these drugs should be staggered throughout the day (see Table 2 below). For COVID treatment, ivermectin is best taken with a meal or just following a meal, for greater absorption.
- Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ): 200 mg twice a day for 5 to 10 days. Best taken with zinc. HCQ may be taken in place of, or together with, ivermectin. While ivermectin should be avoided in pregnancy, the FDA considers HCQ safe in pregnancy. Given the pathway used by the Omicron variant to gain cell entry, HCQ may be the preferred drug for this variant.
- Quercetin (or a mixed flavonoid supplement): 250-500 mg twice a day. Due to a possible interaction between quercetin and ivermectin, these drugs should not be taken simultaneously (i.e., should be staggered at different times of day.) As supplemental quercetin has poor solubility and low oral absorption, lecithin-based and nanoparticle formulations are preferred. (Thorne Quercetin Complex)
- Nigella sativa: If using seeds, take 80 mg/kg once a day (or 400 to 500 mg of encapsulated oil twice a day).
- Honey: 1 g/kg one to two times a day.
- Melatonin: 5-10 mg before bedtime (causes drowsiness). Slow- or extended-release formulations preferred.
- Curcumin (turmeric): 500 mg twice a day. Curcumin has low solubility in water and is poorly absorbed by the body; consequently, it is traditionally taken with full fat milk and black pepper, which enhance its absorption.
- Zinc: 75-100 mg daily. Take with HCQ. Zinc supplements come in various forms (e.g., zinc sulfate, zinc citrate and zinc gluconate).
- Aspirin: 325 mg daily (unless contraindicated).
- Metformin: 500 mg on day 1, 500 mg twice daily on days 2 through 5, then 500 mg in the morning and 1000 mg in the evening up to day 14. (RECOVER 2024, The Lancet 2023, COVID-OUT: NEJM 2022)
- Kefir and/or Bifidobacterium Probiotics. Depending on the brand, these products can be very high in sugar, which promotes inflammation. Look for brands without added sugar or fruit jellies and choose products with more than one strain of lactobacillus and bifidobacteria. Try to choose probiotics that are also gluten-free, casein-free and soy-free. Vitamin C: 500-1000 mg twice a day. (Alternatively, take one to two servings a day of your local organic fruits)
- Home pulse oximeter. Monitoring of oxygen saturation is recommended in symptomatic patients, due to asymptomatic hypoxia. Take multiple readings over the course of the day and regard any downward trend as ominous. Baseline or ambulatory desaturation under 94% should prompt consultation with primary or telehealth provider, or evaluation in an emergency room. (See box for further guidance.)
- Only accept values associated with a strong pulse signal
- Observe readings for 30–60 seconds to identify the most common value
- Warm up extremities prior to taking a measurement
- Use the middle or ring finger
- Remove nail polish from the finger on which measurements are made
Second Line Therapies
(In order of priority/importance)- Nitazoxanide (NTZ): 500 mg twice a day for 5 days.
- Vitamin D3: For patients with acute COVID-19 infection, calcifediol as dosed in table below is suggested.
- Lactoferrin: 100-400 mg daily
- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl): 25-50 mg every 6 hours
- B complex vitamins.
- Fluvoxamine: 25-50 mg twice a day for 1 week. NOTE: Due to serious risks of acute anxiety that may progress to mania or suicidal/violent behavior, this drug should not be prescribed for COVID for longer than two weeks.
- N-acetyl cysteine (NAC): 600-1200 mg orally twice a day.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: 4 g daily. Vascepa (Ethyl eicosapentaenoic acid); Lovaza (EPA/DHA); or alternative DHA/EPA. Vascepa and Lovaza tablets must be swallowed and cannot be crushed, dissolved, or chewed.
Treatment of Current Circulating Omicron variants
Limited data are available on the clinical implications of the current circulating Omicron ‘subvariants’, however these variants have demonstrated ‘neutralization escape’, meaning they have evolved to escape neutralizing antibodies from previous infections or from mRNA injection. Indeed, vaccination appears to be a risk factor for symptomatic disease.If you’ve been exposed to the virus before, you likely have some natural ability to fight it off. We are finding that patients who have not been previously exposed are the ones hit hardest right now.
That doesn’t mean you shouldn’t take steps to protect yourself. The good news is that the advice we’ve been sharing from the FLCCC all along still stands — do what you can to prevent getting ill and if you do get it, treat immediately. Early treatment is critical (below).
High-risk patients should consider:
- The combination of both HCQ and ivermectin
- Nattokinase 2000-4000 FU/day for 15 days OR Apixaban 5 mg daily for 15 days OR Rivaroxaban 10 mg daily for 15 days. The escalated use of anticoagulants should only be considered in patients with a low risk of bleeding. Furthermore, the risk of serious bleeding increases as the number of anticoagulant drugs is increased.
- Spironolactone: 200 mg once daily for 7 days (avoid in patients with impaired renal function)
Oral antibiotic:
- Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 5 days (Doxycycline may act synergistically with ivermectin and might be the antibiotic of first choice.); OR
- Azithromycin (Z-pack) 500 mg day 1, then 250 mg daily for 4 days; OR
- Amoxicillin/Clavulanate (Augmentin) 500 mg/125 mg tablet twice daily for 7 days.
About Ivermectin
Ivermectin is often recognized – 2nd to penicillin – for having the greatest impact on human health. And its discovery won the Nobel Prize in 2015. Ivermectin has an increasing list of indications due to its antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, and is included on the WHO’s Model List of Essential Medicines.
Several studies reported antiviral effects of ivermectin on RNA viruses such as Zika, dengue, yellow fever, West Nile, Hendra, Newcastle, Venezuelan equine encephalitis, chikungunya, Semliki Forest, Sindbis, Avian influenza A, Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome, Human immunodeficiency virus type 1, and COVID 19 virus.
Ivermectin also offer potential benefits in addressing conditions such as cancer, irritable bowel syndrome and scabies.To review the totality of supporting evidence for ivermectin in COVID-19, visit our Ivermectin information page.
Ivermectin is a remarkably safe drug with minimal adverse reactions (almost all minor), however its safety in pregnancy has not been definitively established. Talk to your doctor about use in pregnancy, particularly in the first trimester.Potential drug-drug interactions should be reviewed before prescribing ivermectin.
Ivermectin has been demonstrated to be highly effective against the Omicron variant at a dose of 0.3 to 0.4 mg/kg, when taken early.
Table 1. How to calculate ivermectin dose
Note that ivermectin is available in different strengths (e.g., 3, 6 or 12 mg) and administration forms (tablets, capsules, drops, etc.). Note that tablets can be halved for more accurate dosing, while capsules cannot.

Ordinary Vitamin D3 Does not work in Acute Illness
About FLCCC Alliance
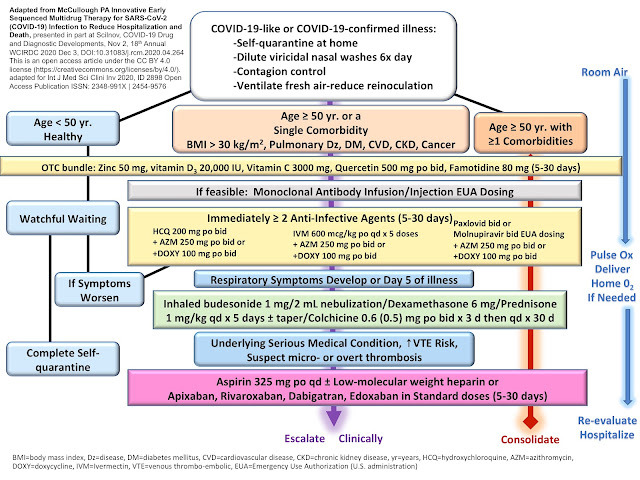
As a group of highly published leaders in critical care with expertise in therapies directed at severe infections, in particular “HAT” therapy first developed by Dr. Paul Marik for the treatment of bacterial sepsis, and along with published high patient survival rates from our centers, we were contacted by equally concerned and motivated colleagues from other specialties.
With the increasing publications in addition to our rapidly accumulating personal clinical experiences and investigations into the pathophysiology of COVID-19 patients, we formulated the MATH+ Hospital Treatment Protocol in March 2020. On August 5, 2020, FLCCC published our findings in the rationale paper Scientific Review of COVID-19 and MATH+.
In October 2020, the FLCCC Alliance identified, based on a review of the recent and rapidly emerging clinical trials evidence, that ivermectin, an anti-parasitic medicine, has highly potent real-world, anti-viral, and anti-inflammatory properties against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. This conclusion is based not only from multiple in-vitro and animal models, but from numerous clinical trials from centers and countries around the world showing repeated, consistent, large magnitude improvements in clinical outcomes when ivermectin is used not only as a prophylactic agent but also in mild, moderate, and even severe disease states. Further, data from large “natural experiments” that appear to have occurred when various regional health ministries and governmental authorities within South American countries initiated “ivermectin distribution” campaigns which then led to temporally associated decreases in case counts and case fatality rates.
Other Potential Treatments
For other potential treatments for COVID-19, check out c19early.com (constantly updated).Other FLCCC Protocols
- I-RECOVER Post Vaccine Protocol
- I-CARE Kids Protocol
- I-CARE Insulin Resistance Protocol
Conclusion and Key Takeaway
Be aware that most of the 'treatment' doses for supplements are above the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) and therefore such doses should not be maintained on a long term basis.
This guide may not be the answer to everything but it could be everything to you or your loved ones.
- Please do not consider these protocols as personal medical advice, but as a recommendation for use by professional providers. Consult with your doctor, share the information on this website and discuss with her/him.
- We are fans and affiliates of FLCCC. We do not represent FLCCC. Any opinions are our own.
- Always see or talk to your doctor before taking these drugs, supplements and over the counter products. Be aware that most of the 'treatment' dosages are above the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) and therefore such dosages should not be maintained on a long term basis.
- Our aim here isn't to replace your doctors' advice. It is intended as a sharing of knowledge and information. Do take note that supplements are not 100% protective or curative against COVID-19.
- You still need to follow the advice given by CDC, WHO and your local authority in terms of local guidelines such as mask wearing, social distancing, vaccination and avoiding crowds. It's better to combine multiple strategies in order to defend yourself against this virus.
- According to US NIH: "...Guidelines should not be considered mandates. The choice of what to do or not to do for an individual patient is ultimately decided by the patient and their provider."
Ivermectin - Nobel Prize Winning Parasite Cleanse Medication
Ivermectin is a Nobel Prize–winning anti-parasitic used worldwide for over 30 years. It works by paralyzing and eliminating parasites through disruption of their nervous systems—helping the body clear a wide range of parasitic infections safely and effectively.
✔ Convenient 6-Month Supply (18 mg each capsule)
✔ FDA-Approved Medication
✔ Doctor-Prescribed



.png)



.png)

I think Table 2 overstates the amounts of Vitamin D by a factor of 10. It mentions "50,000 IU" vitaimin D caps, when I think the highest available is 5,000 IU. I think 50,000 IU might be toxic.
ReplyDeleteI was told ivermectin would cause confusion. Is there anything to that?
ReplyDelete