Long COVID prevention and treatment guidance (2023)
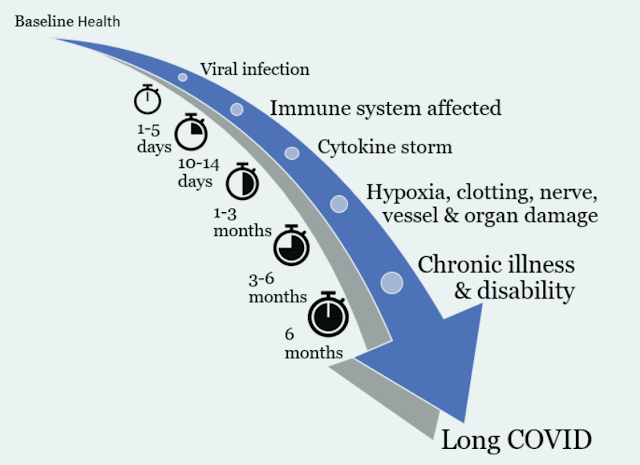
COVID variants appear to be less life threatening in the acute phase than the Alpha strain, but they are causing other disabling medical conditions that affect the quality of life, including brain, nerve and organ damage. Prevention and early intervention are the keys to avoiding this.
In February 2020 the COVID-19 pandemic was officially recognized in the United States. While people may not want to hear about it anymore, COVID-19 continues to spread, causing disability and death from primary and secondary health issues the acute virus causes. Don’t let your guard down yet. This is the “superbug” scientists have been warning us about. SARS was declared a threat in 2017 (link to NIH article in resources listed below). Like other viruses, COVID-19 changes and mutates rapidly and frequently. Newer variants are considered less fatal in the acute phase, but they are lighter, smaller and more contagious than the Alpha strain and they can cause more long-term damage than the Alpha strain. Long COVID will be a risk for many years.
What Is Long COVID?
Many people recover fully within a few days or weeks of being infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. But others have symptoms that linger for weeks, months, or even years after their initial diagnosis. Some people seem to recover from COVID-19 but then see their symptoms return, or they develop new symptoms within a few months. Even people who had no symptoms when they were infected can develop symptoms later. Either mild or severe COVID-19 can lead to long-lasting symptoms.Long COVID, long-haul COVID, post-COVID-19 conditions, chronic COVID, and post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC) are all names for the health problems that some people experience within a few months of a COVID-19 diagnosis. Symptoms of Long COVID may be the same or different than symptoms of COVID-19, and some symptoms are similar to those of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrom (ME/CFS). Long COVID can also trigger other health conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease.
Long COVID statistics:
According to the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), at least 12% of people have been disabled by the COVID-19 spike protein, regardless of the severity of infection or how they were exposed (virus or vaccine).
Based on the 12%, we can estimate that the U.S. has at least 12 million Long COVID cases (up from 10 million in July).
Other researchers estimate the frequency of Long COVID is closer to 30-50%.
Re-infection complication risks were evident in all groups including those who were unvaccinated, had 1 shot, or 2 or more shots prior to the second infection.
Re-infection complication risks persisted in Long COVID, and risks for most sequelae were still evident at 6 months post infection, indicating permanency.
Early intervention strategies with medications, nutritional supplements, and physical and psychological stress management reduce the risks of Long COVID are most effective between 2-12 weeks post infection.
Challenges in diagnosing Long COVID
Most people with COVID-19 get better within a few days to a few weeks after infection. Anyone who was exposed to the spike protein in the natural virus or the vaccine can develop Long COVID regardless of the severity of the infection or the method of exposure. There is no test to diagnose post-COVID conditions, and people may have a wide variety of symptoms that could come from other health problems. This can make it difficult for healthcare providers to recognize post-COVID conditions. Your healthcare provider considers a diagnosis of post-COVID conditions based on your health history, including if you had a diagnosis of COVID-19 either by a positive test or by symptoms or exposure, as well as doing a health examination.Many people infected with COVID-19 get better within weeks, some people continue to experience symptoms that can last months after first being infected or may have new or recurring symptoms at a later time.
This can happen to anyone who has had COVID-19, even if the initial illness was mild. This condition is known as “long COVID.”
Long COVID Symptoms
Long COVID may take weeks or months to present because the damage to the immune system can build gradually over time, starting with the cytokine storm and resulting in multiorgan inflammatory syndrome and autoimmune issues.
People with post-COVID conditions may experience health problems with different combinations of symptoms. These conditions may be temporary or result in permanent disability.
Researchers are finding that repeat infections likely cause more damage to the immune system and body. Early intervention for new infections can reduce the risk of new or worse complications.

1. Fatigue 2. Brain fog 3. Depression 4. Anxiety 5. Insomnia
This list reflects poll results from covidCAREgroup followers with more than 10 thousand responses. Most participants reported a minimum of 3 symptoms.
How do I prevent Long COVID or permanent damage?
Prevention is the best approach!
Prevention through social distancing, handwashing, avoiding crowded spaces with poor ventilation.
Healthy lifestyle habits such as clean eating, stress management, hydration, sleep hygiene, and breathwork.
Nasal flushing, gargling, and swishing daily to wash out viral particles. Nasal flushes help reduce the number of viral particles that get trapped in the higher area of the nose. Listerine has been shown to help reduce viral load in the throat as a safer alternative to hydrogen peroxide.
Vaccination when appropriate.
Early intervention is the key!
If you think you have been infected or re-infected, get tested or do a home test.
If you test positive, ask your doctor about anti-viral medication within the first 5 days of infection.
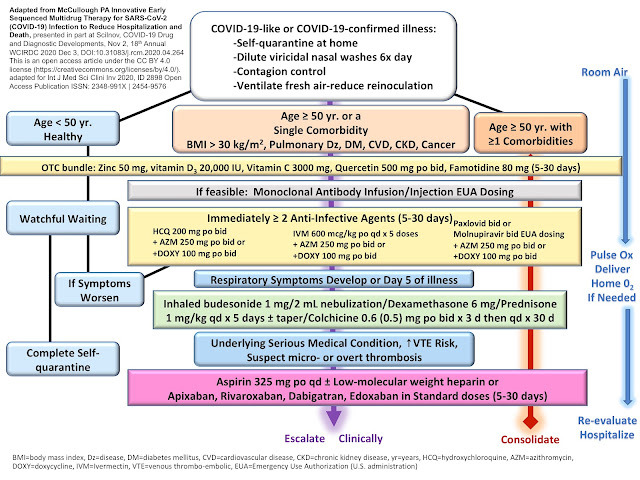
If you get sick, focus on early intervention and utilize the antihistamine, anti-inflammatory, and anticoagulant protocols as well as other resources that are available.
Keep learning and advocating!
If your doctor doesn’t have answers, keep looking.
Remember western medical doctors are trained in medication and surgery and they may not have all of the answers.
You need to take charge of your recovery through education and self-advocacy.
Consider complimentary alternatives such as Chinese medicine, acupuncture, nutrition, counselling or other types of care if you need extra help.
What are the medication protocols for long COVID prevention and treatment?
Talk to your doctor about the top 4 concerns: Histamines, Inflammation, Depression, and Blood Clotting
The antihistamine protocol: Seasonal allergy medicines like Allegra or Zyrtec (H1 blockers) and antacids like famotidine or Pepcid (H2 blockers) to counter the histamine cascade.
The anti-inflammatory protocol: Such as steroids in severe cases, or NSAIDs like ibuprofen or other prescription medications to reduce inflammation, pain, and the risk of damage to nerves and organs.
The antidepressant protocol: SSRI and SNRI medications to reduce depression, anxiety or fatigue.
The anticoagulant protocol: Aspirin, baby aspirin or prescription medications to prevent micro-clotting or deep vein thromboses (DVT) that can cause neural damage, organ damage, or stroke by blocking the flow of blood to vital organs.
Challenges of getting diagnosed:
There is not a specific test to identify Long COVID, so doctors have to rule out other medical issues. Clinical evaluations and results of routine blood tests, chest x-rays, and electrocardiograms may be normal. The symptoms are similar to those reported by people with chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, or other chronic illnesses. People may be misunderstood by their healthcare providers, which can result in delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Some people, especially those who had severe COVID-19, experience multiorgan effects or autoimmune conditions with symptoms lasting weeks or months after COVID-19 illness. Post COVID inflammatory syndrome can involve the organs, nervous system or tissues. There is also a risk of developing new health conditions such as diabetes, heart conditions, or neurological conditions.
People that experienced severe illness, hospitalization, or treatment may develop problems such as post-intensive care syndrome, or PICS. PICS refers to the health effects that may begin when a person is in an intensive care unit (ICU), and which may persist after a person returns home. These effects can include muscle weakness, problems with thinking and judgment, and symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). For people who experience PICS following a COVID-19 diagnosis, it is difficult to determine whether these health problems are caused by a severe illness, the virus itself, or a combination of both.
Researchers cannot predict who develop post-COVID conditions, or what puts them more at risk than other people.
Key medical documentation:
For information about disability benefits follow this link to our article: Important information about applying for disability benefits.

Things you can do to help yourself
Nutrition: Try to eat protein and vitamin rich foods daily.
Avoid chemicals, preservatives, sugars, fast foods, prepared foods and high histamine foods. Don’t skip meals. Your body needs protein , vitamin C, and vitamin D to heal from any injury or illness. A low histamine or low carbohydrate (sugar) diet is recommended by doctors treating Long COVID (PASC), and many people report a reduction in symptoms within 1-3 days of the diet change, including decreases in sneezing, itching or hives, irritable bowel syndrome, body pain, along with a reduction in swelling and inflammation.
Hydration: A minimum of eight 8 oz glasses of plain water daily is recommended.
Avoid drinks with chemical additives. You can easily make a fresh electrolyte drink yourself by adding a dash of mineral rich Epsom salt and a piece a fruit like a raspberry for flavor instead of spending money on commercial drinks like Gatorade that contain chemicals and sit in plastic bottles for long periods of time.Sleep hygiene: Getting 7-9 hours of sleep so your body can repair itself. You need at least 4 hours of uninterrupted sleep to get into the restorative phase of sleep.
Avoid stimulating activities after dinner like thrilling movies or books, arguments, negative news or frustrating stimuli.
If you wake up frequently or with a startle, you may be experiencing drops in your oxygen level, which signal your brain to release adrenaline to force you to take a breath. This could be a temporary inflammation issue or more enduring sleep apnea. Ask your doctor for a sleep study to evaluate your need for a CPAP or BiPAP, a machine that forced air into your lungs when it senses an apneic episode.Stress management: Stress affects every component of your life.
The only thing you can control about stress is your reaction to it. Try to avoid or minimize your exposure to stressful situations: Turn off the news, make family visits that end unpleasantly short, wait for the morning to have intense discussions, let go of things that annoy you but don’t really matter in the big scheme of things, avoid intense conversations or entertainment in the evening.
Exercise within tolerance: Pace yourself and do not push your body to extremes in any way.
For some this may mean seated breathing exercises, walking to the mailbox. Rest when your body says to slow down. Gradually build on your activity endurance as your body cues you to progress.
Breathwork: You can literally stop the fight or flight reaction by taking slow deep breaths.
Deep slow breathing shuts down the adrenaline flow, slows your heart rate, lowers your blood pressure and decreases stress related histamine release. When you do this, your blood reroutes back to your brain and nervous system to allow you to think clearly. It also allows your body to use its energy and oxygen to heal your inflamed nerves and organs.
Long COVID Solutions
It has been a long journey to get here, but every day has brought new scientific advances in addressing Long COVID. We found The Wellness Company with no waiting list for Long COVID telehealth services in the US and expanding internationally soon.
Find Long COVID doctors here.
Find natural supplements developed by the TWC Long COVID medical team at the TWC Shop here, made with pure ingredients in the USA.
Get additional discounts with code ONEDAYMD.
Top recommendations from TWC Long COVID Doctors:
- TWC Spike Formula with Selenium and Nattokinase
- Omega 3 Fatty Acids
- TWC Immune Boost Formula
- TWC Liposomal Vitamin C
- TWC Vitamin D3 with K2
References:








.png)
Comments
Post a Comment