Top 10 Treatments proven to Fight COVID-19 (June 2023)
Top 10 Treatments proven to Fight COVID-19
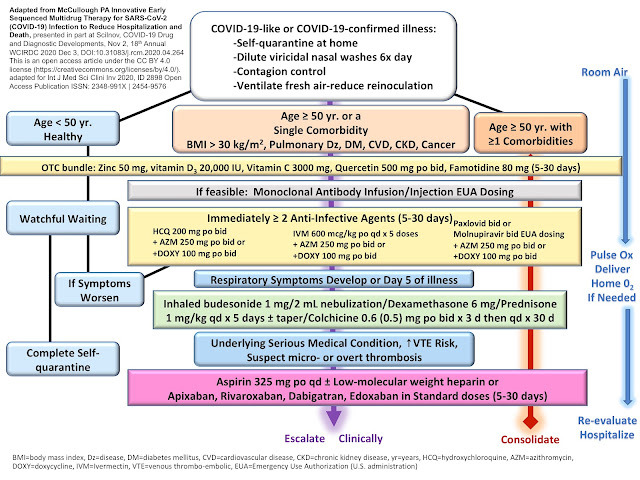
Irrespective of the type of variant, early treatment is more effective than late treatment or no treatment, as shown in the figure below:Although this singular resource has been developed and posted anonymously, one observer commented on Reddit, “It doesn’t really matter who built it, IMO. All studies are referenced/linked.”
The studies for COVID’s readily-available, low-cost, and evidence-based early treatments are divided into sections: Ivermectin, Proxalutamide, Budesonide, Vitamin D, Quercetin, Hydroxychloroquine, Vitamin C, Zinc and many more.
A comprehensive database and global list of COVID-19 treatment studies and outcomes, divided into early treatment and late treatment results, and complete with links and abstracts, is available at this site.
The project has kept up with the recent highly encouraging work on many treatments for COVID-19. Each of these treatment links can be opened to reveal a gold mine of further information.

1. Ivermectin
While this treatment has generated controversy, we have included it in order to acknowledge its popularity and provide a more balanced perspective.- Ivermectin has a number of potentially serious drug-drug interactions. Please check for potential drug interaction at Ivermectin Drug Interactions - Drugs.com. The most important drug interactions occur with cyclosporin, tacrolimus, anti-retroviral drugs, and certain anti-fungal drugs.
- Ivermectin is also lipophilic and therefore, bioavailability is maximised on a full stomach; or best to be taken with meal.
2. Hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine, developed in the 1950s from chloroquine, an old anti-malarial drug, is registered in around 60 countries under trade names such as Plaquenil, Quensyl and Plaquinol.
3. Dietary Supplements (Vitamin D, C, Zinc, Quercetin and Melatonin)
There are more than 100 types of supplements that are being tested for COVID-19. You can review the details of these trials on clinicaltrials.gov.4. Paxlovid and COVID-19
Paxlovid is authorized for adults and children ages 12 and older that weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg). Paxlovid is currently only recommended for people at high risk of developing severe COVID-19. High-risk people include older adults and those with certain medical conditions.
The latest (last updated: April 20, 2023) NIH guidelines recommended Paxlovid as the no. 1 preferred therapy for non-hospitalized patients.
5. Povidone Iodine, Mouthwash and Nasal Spray
Due to the presence of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in the oral gingival epithelium and salivary glands, the human oral cavity may act as a reservoir for SARS-CoV-2. The ACE2 present on the host cell membrane acts as the primary entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2. Evidence indicates that the saliva of SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals contains high amounts of viral RNA and that aerosols formed from the saliva can act as a potential vector for viral transmission.
Povidone iodine (PVP-I) is an antiseptic that has been used for over 150 years. It's already proven that different concentration of PVP-I can deactivate COVID-19 virus.
6. Azithromycin and Antibiotics
Azithromycin is a widely prescribed generic antibiotic. Yes, we do know that COVID-19 is a viral disease and we need an anti-viral and not an anti-bacterial?As of June 2023, there are more than 140 studies that have been launched to investigate the benefits of Azithromycin against COVID-19. You can review the status of these trials on clinicaltrials.gov.
Several trials are testing azithromycin in combination with hydroxychloroquine.
The scientists also found evidence that COVID-19 does not cause a "cytokine storm," so often believed to cause death.
The study was published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation (2023).
"Our study highlights the importance of preventing, looking for and aggressively treating secondary bacterial pneumonia in critically ill patients with severe pneumonia, including those with COVID-19," said senior author Dr. Benjamin Singer, an associate professor of medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a Northwestern Medicine pulmonary and critical care physician.
One potential concern of azithromycin is serious heart side effects. Both drugs can cause abnormal changes in the rhythm of the heart. These can be fatal, particularly for susceptible patients who already have heart problems. Many studies are using EKG tests to closely monitors patients receiving this treatment combination.
While QT-prolonging medication use has been associated with increased risk of death, this risk may be smaller than the potential benefit from treatment of COVID-19 for some patients (American College of Cardiology).
7. Vitamin A
Based on this early treatment mortality studies drug league table below, vitamin A might even out-perform vitamin D, ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine:
.png)
8. Curcumin (Turmeric) - Anti-inflammatory and anti-viral
The improvement rate of 84% has made curcumin ranked No. 6 in the COVID-19 early treatment mortality (death rate) studies league table, better than ivermectin, hydroxychloroquine and quercetin.
.png)
9. Probiotics - Anti-inflammatory
Probiotics are living non-pathogenic microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, can have a positive impact on health. Bacteria in the Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium genera, as well as Streptococcus thermophiles and Saccharomyces boulardii, are examples of common probiotics (Ref).
You can find more than 20 published clinical studies on probiotics and COVID-19 from c19probiotics.com (constantly updated).
The improvement rate of 61% has made probiotics ranked No. 7 in the COVID-19 all mortality (death rate) studies league table, better than ivermectin, hydroxychloroquine and quercetin.
.png)
.png)
10. Other Potential Treatments
.png)
Summary
The combination of quercetin, zinc, vitamin D, vitamin C and melatonin offer a high virus inhibiting and anti-inflammatory potential with a valuable degree of safety at a time of great uncertainty.
That said, based on the above evidence, a combination of vitamin D, quercetin, black seed oil, vitamin A and melatonin might even offer a greater probability of improvement if given as early treatment. Quercetin, zinc, vitamin D and C are part of the FLCCC's I-CARE protocol.
Nutrients and supplements are safer alternatives especially if your risk is low e.g. age below 50 and no other chronic illness. Discuss with your doctor on the benefit vs risk for each treatment. If you are on multiple medications, be aware of supplement-drug interactions that might enhance the possibilities of adverse effects.
However, if your risk is high e.g. age above 60, hypertensive, diabetic and obese; you might wish to consult a doctor and discuss more potent alternatives in the FLCCC's I-CARE protocol.
If you review most of the above studies, you will find a very common theme among most of the studies. A key highlight is that 'early treatment' results tend to be better than 'late treatment' results. Therefore, the most important takeaway is to get 'early treatment'. That said, you should never attempt to self medicate without the guidance of a licensed medical provider. If you are not a medical doctor, you are likely to find the information above overwhelming. Please also follow other precautions and measures (as advised by your local health authorities and doctors) in order to minimize your risk.
Treatments do not replace vaccines and other measures. All practical, effective, and safe means should be used. Elimination is a race against viral evolution. No treatment, vaccine, or intervention is 100% available and effective for all variants.
Z-Stack Supplement
In an effort to make it easier for patients, Dr Zelenko has developed an oral supplement that contains all four key ingredients: vitamin C, quercetin, vitamin D3 and zinc. It’s referred to as 'Z-Stack Supplement'.

Z-Stack Vitamin cocktail provides key ingredients needed in order to help your body fight off this deadly invader. The Z-Stack Vitamins are Kosher certified, GMP certified and made in the USA.
Note: To get 5% OFF, please use this coupon code: drfrancis








.png)
Comments
Post a Comment