FLCCC Protocol for Omicron: Best Treatment for COVID-19 Omicron Variant?
COVID-19 Omicron Variant Treatment?
As of December 2022, subvariants BQ.1.1 and BQ.1 combined are behind nearly 67.9% of cases (CDC). Subvariant BQ.1.1, an offspring of the BA.5, may be able to evade all defense tools we have against COVID-19, leading to potentially more hospitalizations and more cases of long COVID and death.
Experimental antiviral pills - such as Pfizer Inc's (PFE.N) Paxlovid and Merck & Co Inc's (MRK.N) molnupiravir - target parts of the virus that are not changed in Omicron. They will work as effectively against the new variant because these drugs do not target the spike protein – they work by stopping the virus from replicating. However, there is a bigger risk that monoclonal antibodies, such as Regeneron’s treatment, could fail or partially fail because they target parts of the virus that will have mutated.
A combined team of researchers from Leibniz Institute for Primate Research and Friedrich-Alexander University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, both in Germany, has found that the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant BQ.1.1 is resistant to all known monoclonal antibody treatments. In their study, published in The Lancet—Infectious Diseases (Nov 2022), the group tested a host of omicron sublineages against all known antibody treatments.
In their work, the researchers looked at BJ.1, BA.4.6, BA.2.75.2 and BQ.1.1—all subvariants of the omicron strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. They tested each against all of the currently available monoclonal antibody treatments to see how well the treatments are working. They found that all of the variants were resistant to some of the treatments and that BQ.1.1 was resistant to all of them.
This was confirmed by another study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine (Dec 2022).
According to the authors:
"...These results suggest that imdevimab–casirivimab, tixagevimab–cilgavimab, sotrovimab, and bebtelovimab may not be effective against BQ.1.1 or XBB in the clinical setting...These results suggest that remdesivir, molnupiravir, and nirmatrelvir are efficacious against both BQ.1.1 and XBB in vitro..."
Unlike monoclonal antibodies, the antiviral treatment Paxlovid debilitates the virus without needing to fit the virus’ spike protein. That means it should hold up against BQ,1.1, despite its mutations, the NIH said.
Related: Paxlovid vs Bebtelovimab
The FLCCC protocol and Omicron BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 variant
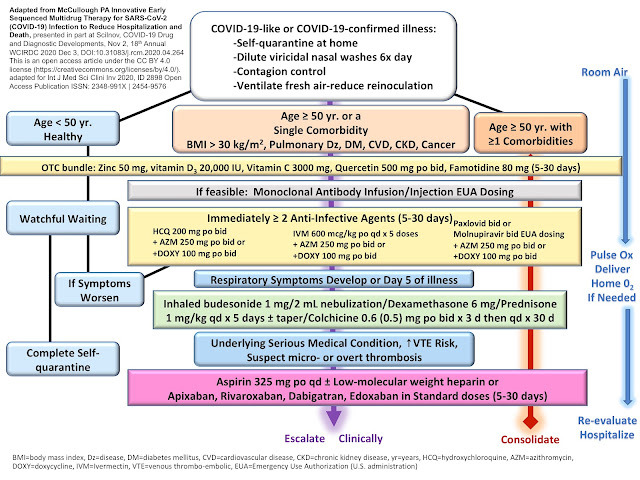
Are the FLCCC protocols effective for the Omicron subvariants? Based on recent clinical experience treating Omicron patients, the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC) modified its early treatment protocol to include hydroxychloroquine as "preferred for Omicron".
The Omicron variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus apparently enters human cells differently than do other variants. Analysis of biological mechanisms for hydroxychloroquine indicate that it has enhanced efficacy for the early treatment of Omicron, especially when coupled with zinc.
The Omicron variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus apparently enters human cells differently than do other variants. Analysis of biological mechanisms for hydroxychloroquine indicate that it has enhanced efficacy for the early treatment of Omicron, especially when coupled with zinc.
Specifically, they recommend hydroxychloroquine (preferred for Omicron) and ivermectin as first line anti-viral agents:
- Ivermectin: 0.4–0.6 mg/kg per dose (take with or after meals) — one dose daily, take for 5 days or until recovered. (Find a Doctor). Use upper dose range if: 1) in regions with more aggressive variants (e.g. Delta); 2) treatment started on or after day 5 of symptoms or in pulmonary phase; or 3) multiple comorbidities/risk factors. (Ref)
- Hydroxychloroquine (preferred for Omicron): 200mg PO twice daily; take for 5 days or until recovered. (Find a Doctor)
Most of the other component treatments in the I-CARE protocol have various mode of actions and may not be affected by the changes in the Omicron variant spike protein.
EARLY TREATMENT PROTOCOL
Based on recent clinical experience treating Omicron patients, the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC) modified its early treatment protocol to include hydroxychloroquine as "preferred for Omicron".
The Omicron variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus apparently enters human cells differently than do other variants. Analysis of biological mechanisms for hydroxychloroquine indicate that it has enhanced efficacy for the early treatment of Omicron, especially when coupled with zinc.
The Omicron variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus apparently enters human cells differently than do other variants. Analysis of biological mechanisms for hydroxychloroquine indicate that it has enhanced efficacy for the early treatment of Omicron, especially when coupled with zinc.
TREATMENT OF OMICRON VARIANTS
First Line Therapies - In order of priority; not all required
The following protocol should be used where Omicron is the predominant circulating strain.
- Ivermectin: 0.4 to 0.6 mg/kg – one dose daily for at least 5 days or until symptoms resolve. If symptoms persist longer than 7 days, consult a healthcare provider. See Table 1 (below) for help with calculating correct dose. Due to a possible interaction between quercetin and ivermectin, these drugs should be staggered throughout the day (see Table 2 below). For COVID treatment, ivermectin is best taken with a meal or just following a meal, for greater absorption.
- Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ): 200 mg twice a day for 5 to 10 days. Best taken with zinc. HCQ may be taken in place of, or together with, ivermectin. While ivermectin should be avoided in pregnancy, the FDA considers HCQ safe in pregnancy. Given the pathway used by the Omicron variant to gain cell entry, HCQ may be the preferred drug for this variant.
- Zinc: 75-100 mg daily. Take with HCQ. Zinc supplements come in various forms (e.g., zinc sulfate, zinc citrate and zinc gluconate).
- Mouthwash: 3 times a day. Gargle three times a day (do not swallow) with an antiseptic-antimicrobial mouthwash containing chlorhexidine, cetylpyridinium chloride (e.g., Scope™, Act™, Crest™) or 1% povidone-iodine.
- Nasal spray with 1% povidone-iodine: 2-3 times a day. Do not use for more than 5 days in pregnancy. If 1% product is not available, dilute the more widely available 10% solution (see box) and apply 4-5 drops to each nostril every 4 hours.
- Melatonin: 5-10 mg before bedtime (causes drowsiness). Slow- or extended-release formulations preferred.
- Nigella sativa: If using seeds, take 80 mg/kg once a day (or 400 to 500 mg of encapsulated oil twice a day).
- Aspirin: 325 mg daily (unless contraindicated). NAC can be considered as alternative.
- Probiotics. NOTE: Depending on the brand, these products can be very high in sugar, which promotes inflammation. Look for brands without added sugar or fruit jellies and choose products with more than one strain of lactobacillus and bifidobacteria. Try to choose probiotics that are also gluten free, casein free and soy free.
- Vitamin C: 500-1000 mg twice a day
- Home pulse oximetry: Monitoring of oxygen saturation is recommended in symptomatic patients, due to asymptomatic hypoxia. Take multiple readings over the course of the day and regard any downward trend as ominous. Baseline or ambulatory desaturation under 94% should prompt consultation with primary or telehealth provider, or evaluation in an emergency room.
COVID-19 is a highly dynamic topic. Please refer to the latest FLCCC I-CARE protocol (constantly updated).
Table 1. How to calculate ivermectin dose


Related:

Related:
Key Takeaways
The most important takeaway is to start treatment 'early'. As soon as you have symptoms, consult your healthcare provider and start treatment as early as possible. If treatment is delayed i.e. after 5 days of symptoms, your chances of severe COVID are higher.
For post-covid or long covid syndrome, check out FLCCC's I-Recover Post-COVID Protocol.
Related:
Z-Stack Supplement
In an effort to make it easier for patients, Dr Zelenko has developed an oral supplement that contains all four key ingredients: vitamin C, quercetin, vitamin D3 and zinc. It’s referred to as 'Z-Stack Supplement.

Z-Stack Vitamin cocktail provides key ingredients needed in order to help your body fight off this deadly invader. The Z-Stack Vitamins are Kosher certified, GMP certified and made in the USA.
The cost of the Z-STACK vitamin cocktail is $55 per bottle for a one month supply.
The cost of the Z-STACK vitamin cocktail is $55 per bottle for a one month supply.
Where to buy Z-Stack: Z-stack is available on Dr Zelenko's website. Here is the link: Z Stack Supplement.
Note: To get 5% OFF, please use this coupon code: DRFRANCIS






.png)

Comments
Post a Comment