Dr Zelenko Fact Check: Has Dr. Zelenko Successfully Treated Coronavirus Patients?
The Claim
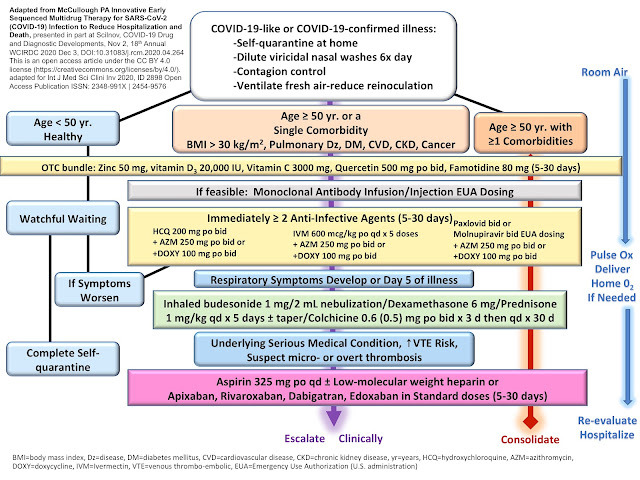
I developed the following treatment protocol in the pre-hospital setting and have seen only positive results. […]
The rationale for my treatment plan is as follows. […] We know that hydroxychloroquine helps Zinc enter the cell. We know that Zinc slows viral replication within the cell. Regarding the use of azithromycin, I postulate it prevents secondary bacterial infections. These three drugs are well known and usually well tolerated, hence the risk to the patient is low.
Since last Thursday, my team has treated approximately 350 patients in Kiryas Joel and another 150 patients in other areas of New York with the above regimen. Of this group and the information provided to me by affiliated medical teams, we have had ZERO deaths, ZERO hospitalizations, and ZERO intubations. In addition, I have not heard of any negative side effects other than approximately 10% of patients with temporary nausea and diarrhea.
In sum, my urgent recommendation is to initiate treatment in the outpatient setting as soon as possible in accordance with the above. Based on my direct experience, it prevents acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), prevents the need for hospitalization and saves lives.
Evidence
The Science behind Zinc, Quercetin, Vitamin D and C
Some media channels argue that there is very little evidence to support the use of quercetin, zinc, vitamin D and C in supporting the immune system. We have included the scientific evidence together with the sources and references in this article below and we leave it up to you, the reader, to decide who is the 'fact-checker'.Quercetin has been shown to inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production as well as inflammation due to its antioxidant properties, amongst others. By inhibiting destructive inflammation and potentially the entire cascade, quercetin may prevent severe damage to the respiratory system amongst other organs (source).
Zinc is a well known supplement that is generally contained in standard multivitamins. It provides immune support amongst other functions. Zinc inhibits coronavirus replication and is a general stimulant of antiviral immunity (source). Higher levels of intracellular zinc showed to increase intracellular pH; which affect on RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and decreases the replication mechanism of RNA viruses (e.g. COVID-19). Therefore, zinc ionophores (e.g. Quercetin) can likely be used with zinc supplement to act as antiviral against many RNA viruses including influenza and COVID-19. Suggested benefits of zinc supplementation along with zinc ionophores to prevent and treat COVID-19 and other respiratory tract infections are supported by countless studies (source). In most cases, prophylactic and early use of zinc supplementation was more effective than late therapeutic proceedings. Up to 30% of the everyday respiratory infections, briefly named “common cold,” are due to infections with coronaviruses. Studies showed reduced symptom severity, reduced frequency, and duration of the common cold after zinc administration depending on dosage, zinc compound and the start time after initial symptoms (source).
In short, a balanced zinc homeostasis is essential. Zinc supplementation improves the mucociliary clearance, strengthens the integrity of the epithelium, decreases viral replication, preserves antiviral immunity, attenuates the risk of hyper-inflammation, supports anti-oxidative effects and thus reduces lung damage and minimizes secondary infections. Especially older subjects, patients with chronic diseases and most of the remaining COVID-19 risk groups would most likely benefit.
The link between vitamin D and viral infections arose from the observation of the seasonality of vitamin D with lower levels in the winter and concomitant increases in influenza. Conversely, in summer, serum levels of Vitamin D increase and influenza virtually disappears, except during pandemics. Even in pandemics, most deaths occur during cold months.
Hydroxychloroquine
The evidence tracking on Hydroxychloroquine versus COVID-19 is available at c19hcq.com (constantly updated).
Azithromycin is a widely prescribed generic antibiotic. While it's mainly used to fight bacteria, not viruses, there is some research suggesting the drug has antiviral properties.
As of December 2021, there are more than 120 studies that have been launched to investigate the benefits of Azithromycin against COVID-19. You can review the status of these trials on clinicaltrials.gov. Several trials are testing azithromycin in combination with hydroxychloroquine.
One potential concern is serious heart side effects. Both drugs can cause abnormal changes in the rhythm of the heart. These can be fatal, particularly for susceptible patients who already have heart problems. Many studies are using EKG tests to closely monitors patients receiving this treatment combination.
While QT-prolonging medication use has been associated with increased risk of death, this risk may be smaller than the potential benefit from treatment of COVID-19 for some patients (American College of Cardiology).
About Dr Vladimir Zelenko
He graduated with a B.A. degree with high honors in Chemistry from Hofstra University. After receiving an academic scholarship to attend S.U.N.Y. at Buffalo School of Medicine, he earned his M.D. degree in May 2000. Dr. Zelenko completed his family medicine residency at South Nassau Communities Hospital in Oceanside, N.Y. in May 2004. Since then, Dr. Zelenko has practiced family medicine in New York’s Hudson Valley. He has been described by his patients as like a family member to thousands of families, and is a medical adviser to the volunteer ambulance corps in Kiryas Joel, New York.When asked about studies that seemed to discredit the efficacy of HCQ in treating the Chinese coronavirus, Zelenko explained “You don’t fire a gun without a bullet in it and then say the gun doesn’t work when you don’t kill the target. The studies that were done on HCQ did not include the use of Zinc. HCQ is what opens the cell and enables Zinc to attack the virus. One is not effective without the other, or without a suitable substitute for HCQ. The studies were designed to fail.”
Dr. Zelenko says that both prophylaxis measures and actual case treatments need to be customized to the individual. As a general rule, he says, those people who are in the higher risk groups, both by age and by other pre-existing conditions, require more aggressive actions on both the preventative and diagnostic side.
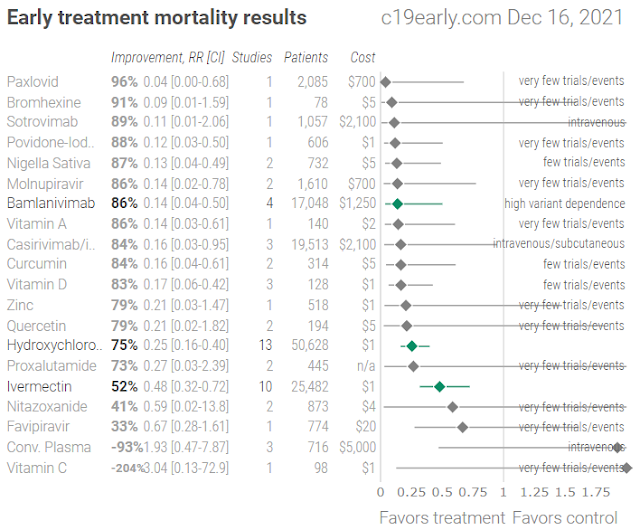
“This virus remains relatively stable inside the host for about the first five days,” Zelenko says. “After that it starts to multiply rapidly. It also starts to migrate from sinus to lungs and cardio areas where involvement becomes more severe and treatment becomes more difficult. The key is early intervention.” Zelenko again mentioned his 84% success rate in high-risk patients.






.png)

Actually Quercetin has few more unmentioned properties, similar to antibody, it likes to bind: Molecular docking analysis to determine the putative binding sites of selected inhibitors on SARS-CoV-2S (spike protein), S2 Domain. with one of highest binding affinity among tested group ((8.5 kcal/mol)) in paper https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7441770/#!po=10.7143 thus interfering with binding properties of S1 spike protein interaction with ACE2 in humans!
ReplyDelete