Quercetin and Zinc: Zelenko Treatment Protocol
As of July 2024, more than 35 studies on the topic of zinc and COVID-19 (c19zinc.com) (constantly updated) and more than 10 studies on quercetin and COVID-19 have been published (c19quercetin.com).
Dr. Zelenko’s main hypothesis based on the data showing that early intervention and treatment of high-risk patients with COVID-19 results in significantly few hospitalizations and deaths. This treatment regimen involving zinc, low-dose hydroxychloroquine, and azithromycin (published in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents) is also apparently known as, “The Zelenko Protocol.”
Quercetin and Zinc
Quercetin is a natural antihistamine and anti-inflammatory plant pigment that boosts your immune system and may work to control viral replication, according to some research. It allows zinc to exert its proven antiviral properties; in treating COVID-19, quercetin may also lower inflammation, help clear mucus, prevent ventilator-induced damage, support immunity and might also be a valuable candidate for treatment of malaria and different kinds of leishmaniasis (Journal of Parasitic Diseases 2023).
Foods high in quercetin include onions, kale, tomatoes, broccoli, asparagus, berries, red wine, citrus fruits, cherries, and tea.
According to the research, quercetin has been shown to help fight obesity, Type 2 diabetes, circulatory dysfunction, chronic inflammation and mood disorders. It has even been found to help lower blood pressure. Researchers have found that quercetin can trigger tumor regression and begin the process of apoptosis. This is programmed cell death, without which cells can grow uninterrupted and develop into cancerous growths.
Zelenko Covid-19 Prophylaxis Protocol
- Low Risk Patients: Young healthy people do not need prophylaxis against Covid-19. In young and healthy people, this infection causes mild cold-like symptoms. It is advantageous for these patients to be exposed to Covid-19, build up their antibodies and have their immune system clear the virus. This will facilitate the development of herd immunity and help prevent future Covid-19 pandemics. However, if these patients desire prophylaxis against Covid-19, then they should take the protocol noted below.
- Moderate Risk Patients: Patients from this category are healthy but have high potential viral-load exposure. This group includes medical personnel, caregivers of high-risk patients, people who use public transportation, first responders and other essential personnel who are crucial to the continued functioning of society. These patients should be encouraged to take prophylaxis against Covid-19 in accordance with the protocol noted below.
- High Risk Patients: Patients are considered high risk if they are over the age of 45, or if they are younger than 45 but they have comorbidities, that is, they have other health conditions that put them at risk. These patients have between a 5 to 10% mortality rate if they are infected with Covid-19. These patients should be strongly encouraged to take prophylaxis against Covid-19 in accordance with the protocol noted below.
- Zinc (elemental) 25mg 1 time a day (PubMed)
- Vitamin D3 5000 iu 1 time a day (vdnmeta.com)
- Vitamin C 1000 mg 1 time a day (PubMed)
- Quercetin 500mg 1 time a day
- Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) 200mg once a day for 5 days, then HCQ 200 mg one time a week (ScienceDirect) (Find a Doctor)
- Vitamin D3 5000 IU/day
- Zinc 25 mg/day | How much zinc to take with hydroxychloroquine?
- Although ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) are relatively safe drugs, they are still synthetic chemicals that can have side effects. Vitamin D, C, Zinc and Quercetin are nutrients that your body require for optimal health. Nutrients are safer alternatives especially if your risk is low e.g. age below 50 and no other chronic illness. Discuss with your doctor on the benefit vs risk for each treatment.
- Some 200 peer-reviewed studies (C19Study.com) by government and independent researchers deem HCQ safe and effective against Coronavirus, especially when taken prophylactically or when taken in the initial stages of illness along with zinc and azithromycin. Unfortunately, some of the RCTs that have been conducted to date used toxic doses of HCQ and/or were given very late in the disease.
- Inorganic zinc such as zinc sulfate, is not as effective or useable by your body as chelated zinc sources. Zinc lozenges are preferred so that the tissues of the nose and throat are rich in zinc as soon as they encounter the virus.
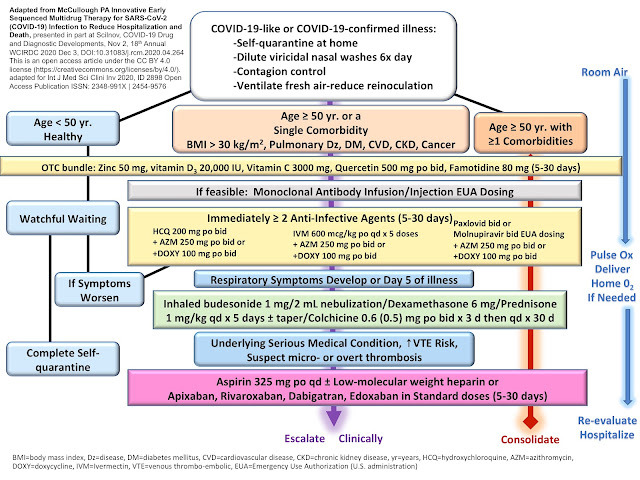
Zelenko Protocol - Treatment Plan for Patients with Covid-19 symptoms
Fundamental Principles (Dr Zelenko Protocol When to Start)
Patient Categories
Low risk patient - Younger than 45, no co-morbidities, and clinically stableHigh risk patient - Older than 45, younger than 45 with co-morbidities, or clinically unstable
Treatment Options
Low risk patients - over the counter options:Supportive care with fluids, fever control, and rest
Alternative for Quercetin: Epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG) 400mg 1 time a day for 7 days (J. Agric. Food Chem)
- Zinc (Elemental) 50-100mg once a day for 7 days
- Vitamin C 1000mg 1 time a day for 7 days
- Vitamin D3 10,000 iu once a day for 7 days or 50,000 iu once a day for 1-2 days
- Azithromycin (Z Pack) 500mg 1 time a day for 5 days (Clin Drug Investig) OR Doxycycline 100mg 2 times a day for 7 days
- Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) 200mg 2 times a day for 5-7 days (ScienceDirect)
Ivermectin 0.4-0.5mg/kg/day for 5-7 days (ivmmeta.com). (Find a Doctor)
Hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin combined? Either or both HCQ and IVM can be used, and if one only, the second agent may be added after about 2 days of treatment if obvious recovery has not yet been observed etc.
If HCQ is not available, Quercetin 500mg 3 times a day for 7 days OR
EGCG 400mg 2 times a day for 7 days
- Dexamethasone 6-12mg 1 time a day for 7 days OR Prednisone 20mg twice a day for 7 days, taper as needed (not suitable during viral phase)
- Budesonide 1mg/2cc solution via nebulizer twice a day for 7 days (not suitable during viral phase)
- Blood thinners (i.e. Lovenox, Eliquis, Xarelto, Pradaxa, Aspirin) (Amazon)
- Colchicine 0.6mg 2-3 times a day for 5-7 days (MedRxiv 2021)
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Home IV fluids and oxygen
- Curcumin: 500 mg twice a day (Ref) (Amazon)
- Fluvoxamine: 50 mg twice daily for 10–14 days. Add to ivermectin if: 1) minimal response after 2 days of ivermectin; 2) in regions with more aggressive variants; 3) treatment started on or after day 5 of symptoms or in pulmonary phase; or 4) numerous co-morbidities/risk factors. Avoid if patient is already on an SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor). If you can’t get fluvoxamine (Luvox), using 30mg once a day of fluoxetine (Prozac) is equally effective (equivalent to 50mg twice a day of fluvoxamine).
- Pulse Oximeter: Monitoring your oxygen saturation with a pulse oximeter and to go to the hospital if you get below 94%. (Amazon)
- Mouthwash: 3 x daily – gargle (do not swallow) antiseptic mouthwash with cetylpyridinium chloride (e.g. Crest, Scope mouthwash™) or povidone/iodine 1 % solution as alternative (Betadine® Antiseptic Sore Throat Gargle™). (Ref)
- Nasal Spray: Xlear Nasal Spray with Xylitol (Ref) (Amazon)
- Aspirin: 325 mg/day unless contraindicated. (Amazon) (not suitable during viral phase)
- NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine) 500 mg twice a day.
- Bromhexine 8 mg three times a day (Ref) (Lazada Malaysia*)
- Precautionary Note: Ivermectin has a number of potentially serious drug-drug interactions. Please check for potential drug interaction at Ivermectin Drug Interactions - Drugs.com. The most important drug interactions occur with cyclosporin, tacrolimus, anti-retroviral drugs, and certain anti-fungal drugs.
- Due to the possible drug interaction between quercetin and ivermectin (may increase ivermectin levels), these drugs should not be taken simultaneously (i.e. should be staggered morning and night).
- Ivermectin is also lipophilic and therefore, bioavailability is maximised on a full stomach; or best to be taken with meal.
- Vitamin D3 RDA (Recommended Daily Allowance) is 800–1000 IU/day. The safe upper-dose daily limit is likely < 4000 IU/day. Be aware that most of the 'treatment' dosages for nutrients are above the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) and therefore such dosages should not be maintained on a long term basis.
- Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with an increased risk of acquiring COVID-19 and from dying from the disease. Vitamin D supplementation may therefore prove to be an effective and cheap intervention to lessen the impact of this disease, particularly in vulnerable populations, i.e. the elderly and obese.
- When Is the Best Time to Take Vitamin D? Morning or Night? It is possible that increasing vitamin D levels during the day may act, in part, as a signal that suppresses melatonin generation (source). Therefore, it's better to take vitamin D (with meal) during the day and melatonin to be taken just before bedtime.
- It is likely that vitamin C and quercetin have synergistic prophylactic benefit. Quercetin should be used with caution in patients with hypothyroidism and TSH levels should be monitored.
- Please consult with a qualified doctor and only use human ivermectin. Ivermectin for animals contain excipients (binding and storage compounds such as polyethylene glycol (PEG)) that are known to cause liver failure in high doses.
Early Treatment Prevents 'Long Haul' Side Effects
According to Dr Zelenko:
Others developed ARDS or catastrophic lung damage and pneumonias, and others just are not themselves. I don't know how to describe it, but it ate away part of their souls. They're not the same people. There's depression, there's lack of energy. There's a psychological impact as well.
So, it's not that I don't deal with long-haulers, I do. But the way to prevent the long-hauler syndrome is to intervene within the first five days, with appropriate antiviral medication in high-risk patients. That is 100% successful."
Z-Stack Supplement
In an effort to make it easier for patients, Dr Zelenko has developed an oral supplement that contains all four key ingredients: vitamin C, quercetin, vitamin D3 and zinc. It’s referred to as 'Z-Stack Supplement'.

Z-Stack Vitamin cocktail provides key ingredients needed in order to help your body fight off this deadly invader. The Z-Stack Vitamins are Kosher certified, GMP certified and made in the USA.
Note: To get 5% OFF, please use this coupon code: ONEDAYMD
About Dr Vladimir Zelenko
He graduated with a B.A. degree with high honors in Chemistry from Hofstra University. After receiving an academic scholarship to attend S.U.N.Y. at Buffalo School of Medicine, he earned his M.D. degree in May 2000. Dr. Zelenko completed his family medicine residency at South Nassau Communities Hospital in Oceanside, N.Y. in May 2004. Since then, Dr. Zelenko has practiced family medicine in New York’s Hudson Valley. He has been described by his patients as like a family member to thousands of families, and is a medical adviser to the volunteer ambulance corps in Kiryas Joel, New York.When asked about studies that seemed to discredit the efficacy of HCQ in treating the Chinese coronavirus, Zelenko explained “You don’t fire a gun without a bullet in it and then say the gun doesn’t work when you don’t kill the target. The studies that were done on HCQ did not include the use of Zinc. HCQ is what opens the cell and enables Zinc to attack the virus. One is not effective without the other, or without a suitable substitute for HCQ. The studies were designed to fail.”
Dr. Zelenko says that both prophylaxis measures and actual case treatments need to be customized to the individual. As a general rule, he says, those people who are in the higher risk groups, both by age and by other pre-existing conditions, require more aggressive actions on both the preventative and diagnostic side.
“This virus remains relatively stable inside the host for about the first five days,” Zelenko says. “After that it starts to multiply rapidly. It also starts to migrate from sinus to lungs and cardio areas where involvement becomes more severe and treatment becomes more difficult. The key is early intervention.” Zelenko again mentioned his 84% success rate in high-risk patients.
References:
1.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S09248579203042582.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7365891/
3.https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jf5014633
4.https://vdmeta.com/
5.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7318306/
6.https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jf5014633
7.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924857920304258
8.https://ivmmeta.com/
9.https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
10.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7392554/
Scientific Papers from Dr. Zelenko and his collaborators
- Kory, Pierre MD, Meduri, Gianfranco Umberto MD, Varon, Joseph MD, Iglesias, Jose DO, Marik, Paul E. MD: Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics: May Jun 2021 - Volume 28 - Issue 3 - p e299-e318
- R. Derwand, M. Scholz, "Does zinc supplementation enhance the clinical efficacy of chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine to win today's battle against COVID-19?", Medical Hypotheses 142 (2020), 109815
- Scholz, M.; Derwand, R.; Zelenko, V. "COVID-19 outpatients - early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective case series study", International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 56 (2020), 106214 [press release]
- Peter A. McCullough, Ronan J.Kelly, Gaetano Ruocco, Edgar Lerma, James Tumlin, Kevin R.Wheelan, Nevin Katz, Norman E. Lepor, Kris Vijay, Harvey Carter, Bhupinder Singh, Sean P.McCullough, Brijesh K.Bhambi, Alberto Palazzuoli, Gaetano M.De Ferrari, Gregory P.Milligan, TaimurSafder, Kristen M.Tecson, Harvey A.Risch: "Pathophysiological Basis and Rationale for Early Outpatient Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Infection", The American Journal of Medicine 134 (2020), 16-22
- Peter A. McCullough, Paul E. Alexander, Robin Armstrong, Cristian Arvinte, Alan F. Bain, Richard P. Bartlett, Robert L. Berkowitz, Andrew C. Berry, Thomas J. Borody, Joseph H. Brewer, Adam M. Brufsky, Teryn Clarke, Roland Derwand, Alieta Eck, John Eck, Richard A. Eisner, George C. Fareed, Angelina Farella, Silvia N. S. Fonseca, Charles E. Geyer, Jr., Russell S. Gonnering, Karladine E. Graves, Kenneth B. V. Gross, Sabine Hazan, Kristin S. Held, H. Thomas Hight, Stella Immanuel, Michael M. Jacobs, Joseph A. Ladapo, Lionel H. Lee, John Littell, Ivette Lozano, Harpal S. Mangat, Ben Marble, John E. McKinnon, Lee D. Merritt, Jane M. Orient, Ramin Oskoui, Donald C. Pompan, Brian C. Procter, Chad Prodromos, Juliana Cepelowicz Rajter, Jean-Jacques Rajter, C. Venkata S. Ram, Salete S. Rios, Harvey A. Risch, Michael J. A. Robb, Molly Rutherford, Martin Scholz, Marilyn M. Singleton, James A. Tumlin, Brian M. Tyson, Richard G. Urso, Kelly Victory, Elizabeth Lee Vliet, Craig M. Wax, Alexandre G. Wolkoff, Vicki Wooll, Vladimir Zelenko."Multifaceted highly targeted sequential multidrug treatment of early ambulatory high-risk SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19)", Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine 21 (4) (2020), 517-530
- Brian C. Procter, Casey Ross, Vanessa Pickard, Erica Smith, Cortney Hanson, Peter A. McCullough. "Clinical outcomes after early ambulatory multidrug therapy for high-risk SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection", Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine 21 (4) (2020), 611-614






.png)

NAC works pretty well for post-covid.
ReplyDeleteThank you for everything you are doing for us mere plebs. I am trying to follow your protocol and have some success. My question to you...I bought Vitamin D3 and it is measured in 500ME... I am in Russia. How do I convert this to mg's???
ReplyDeleteThank You so very much for everything..
ReplyDeleteCan you take the Protocol AFTER the vaccine for detoxification?
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
DeletePlease refer to Treatment for Post Vaccine protocol
Delete