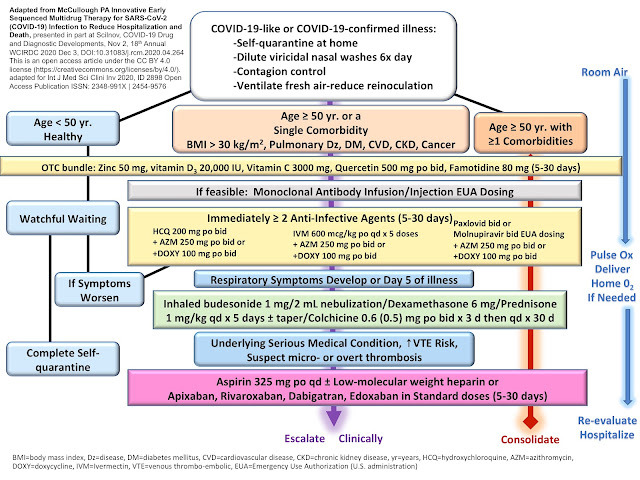
Vitamin A and COVID-19: Studies Show Vitamin A is Critical
Vitamin A plays a key role in regulating the immune system, development of lung tissue and repair of infection-related damage. To better understand its potential role in COVID-19, University Hospital Muenster researchers compared vitamin A blood plasma levels in critically ill and recovering COVID-19 patients. The study is one of the first to differentiate between unbound free vitamin A, retinol-binding protein (RBP) and total vitamin A. They found that critically ill patients in the acute phase of COVID-19 showed significantly decreased total vitamin A and RBP-bound levels compared to patients who were recovering. Although these results support previous studies that have shown vitamin A deficiency in patients with acute infections, the researchers say that more work is needed to understand how this deficiency might affect COVID-19 disease progression.
Richard Vollenberg will present this research on-demand starting at noon on Tuesday, June 14, during NUTRITION 2022 LIVE ONLINE (presentation details).

.png)
The COVIDENCE UK study (published in Thorax, BMJ), studied more than 15,000 participants in UK from May 2020 to February 2021. Out of the 15,227 participants, 2.9% tested positive (446 cases).
Prospective survey-based study with 15,227 people in the UK, showing relatively lower risk of COVID-19 cases with vitamin A. However, it was not statistically significant.

.png)
Richard Vollenberg will present this research on-demand starting at noon on Tuesday, June 14, during NUTRITION 2022 LIVE ONLINE (presentation details).
Please note that abstracts presented at NUTRITION 2022 LIVE ONLINE were evaluated and selected by a committee of experts but have not generally undergone the same peer review process required for publication in a scientific journal. As such, the findings presented should be considered preliminary until a peer-reviewed publication is available.
Vitamin A and COVID-19
As of July 2022, there are 8 published studies of vitamin A for treatment and prevention of COVID-19 (c19early.com/va).

Vitamin A for COVID-19 Prevention
As you can see from the table and chart below, vitamin A is one of the most studied nutraceutical for prevention. The league table below suggests that vitamin A may be a better candidate as compared to vitamin D in terms of prevention. Although quercetin appears to be the most promising nutrient, the number of patients studied is relatively smaller as compared to vitamin A or D.
.png)
The COVIDENCE UK study (published in Thorax, BMJ), studied more than 15,000 participants in UK from May 2020 to February 2021. Out of the 15,227 participants, 2.9% tested positive (446 cases).

Vitamin A for Early Treatment
If you refer to the C19Early.com league table below, the effectiveness of vitamin A as early treatment out-performs many other OTC (over the counter) compounds such as vitamin D, melatonin and povidone-iodine. That said, the number of patients studied is still relatively small.
.png)
Key Takeaways
Aside from supplements and preventive treatments, there are other ways that may help improve immune response and to prevent you from catching the coronavirus.
- Abundant evidence suggests that eating whole in fruits, vegetables and whole grains—all rich in networks of naturally occurring antioxidants and their helper molecules—provides protection against free radicals.
- Vaccination
- Getting Enough Sleep
- Avoid sugar, red meat and processed foods.
- Take steps to avoid infection, such as washing your hands frequently and cooking meats thoroughly.
- Try to minimize stress.
- Drink enough water to keep your body hydrated.
- Avoid drinking excess alcohol and stop smoking.
- Avoid crowded areas especially in-door.
- Regular outdoor physical activity. (Ref)
- Wear protective face mask. This is to protect not only yourself but others.
- Consult your nearest local healthcare provider if you have any doubt.





.png)

Comments
Post a Comment