Home Isolation Medicine for COVID positive 2022
Providing care at home for a person sick with positive COVID-19? Or caring for yourself at home?
However, older adults and people of any age with existing medical conditions should call their doctor as soon as symptoms start. These factors put people at greater risk of becoming seriously ill with COVID-19.
Follow the doctor's recommendations about care and home isolation for yourself or your loved one. Talk to the doctor if you have any questions about treatments.
It's also important to consider how caring for a sick person might affect your health. If you are older or have an existing medical condition, such as heart or lung disease or diabetes, you may be at higher risk of serious illness with COVID-19. You might consider isolating yourself from the sick person and finding another person to provide care.

All the component medicines are FDA-approved (except ivermectin), inexpensive, readily available and have been used for decades with well-established safety profiles.
Dual anti-androgen Therapy
Fluvoxamine: 50 mg twice daily for 10 days.
Consider fluoxetine (Prozac) 30mg daily for 10 days as an alternative (it is often better tolerated).
Avoid if patient is already on an SSRI.
Can over the counter medications help with symptoms of COVID-19?
Understand home isolation medicine and what medications can I take to relieve the symptoms of COVID-19. Here's what you need to know.
At-home treatment
Most people who become sick with COVID-19 will only experience mild illness and can recover at home. Symptoms might last a few days, and people who have the virus might feel better in about a week.However, older adults and people of any age with existing medical conditions should call their doctor as soon as symptoms start. These factors put people at greater risk of becoming seriously ill with COVID-19.
Follow the doctor's recommendations about care and home isolation for yourself or your loved one. Talk to the doctor if you have any questions about treatments.
It's also important to consider how caring for a sick person might affect your health. If you are older or have an existing medical condition, such as heart or lung disease or diabetes, you may be at higher risk of serious illness with COVID-19. You might consider isolating yourself from the sick person and finding another person to provide care.
Home Treatment Recommendations for COVID
While it can be difficult to find a doctor who is willing to actually treat COVID-19, many of those who are willing are making full use of telemedicine.
You can find a listing of doctors who can prescribe necessary home isolation medications on Find a Provider post. You can also find home isolation medication protocol on Prevention and early at-home treatment,
Other protocols that have great success are:This is a load of information to read, review and understand, especially if you are fatigued and sick with COVID or have a family member struggling. So, we have reviewed all the protocols and believe the FLCCC one is the easiest and most effective to follow. We’ve posted it below.
Other protocols that have great success are:This is a load of information to read, review and understand, especially if you are fatigued and sick with COVID or have a family member struggling. So, we have reviewed all the protocols and believe the FLCCC one is the easiest and most effective to follow. We’ve posted it below.
The I-MASK+ protocol has been updated several times and below is their latest version (version 19: Jan 19, 2022).
Updates:
While we carefully lay out the evidence in this article, we leave it up to you, the reader, to decide. That said, always consult your trusted medical professional before you take any medication or supplement. Do not self-medicate.

McCullough et al. Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine, 2020
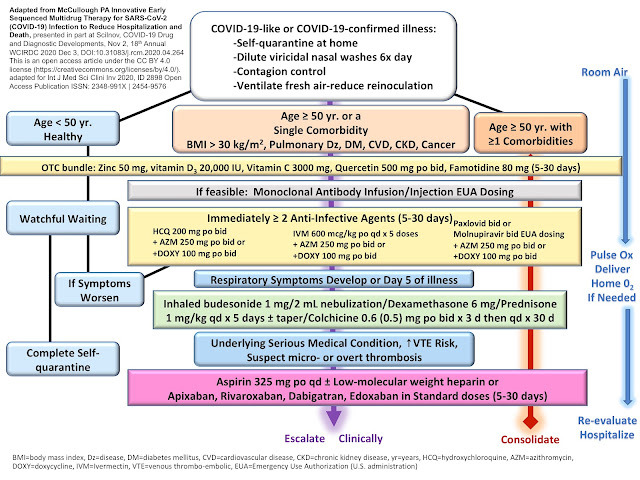
FLCCC (Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care) I-MASK+ Protocol
I-MASK+ Prevention & Early Outpatient Treatment Protocol for COVID-19 was designed for use as a prevention and in early outpatient treatment, for those who test positive for COVID-19. Component nutrients include vitamin D, C, melatonin, quercetin and zinc.
All the component medicines are FDA-approved (except ivermectin), inexpensive, readily available and have been used for decades with well-established safety profiles.
PREVENTION PROTOCOL
Should I take ivermectin as a prophylaxis? For preventive measures, the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Working Group (FLCCC) I-MASK+ protocol recommends:
Anti-Virals & AntiSeptics
- Gargle mouthwash: 2 x daily – gargle (do not swallow) antiseptic mouthwash with cetylpyridinium chloride (e.g. Crest mouthwash, Scope mouthwash™, Act, Colgate mouthwash) or povidone iodine 1 % solution as alternative (e.g. Betadine® Antiseptic Sore Throat Gargle™).
- lvermectin
- Chronic Prevention: 0.2 mg/kg per dose (take with or after a meal) — twice a week for as long as disease risk is elevated in your community (Ref). Alternative: Hydroxychloroquine – 200 mg tablet daily.
- Post COVID-19 Exposure Prevention: 0.4 mg/kg per dose (take with or after a meal) — one dose today, repeat after 48 hours. Alternative: Hydroxychloroquine – 400mg twice day on day 1, then 200mg twice a day on Days 2 and 3.
Related:
Immune Fortifying / Supportive Therapy
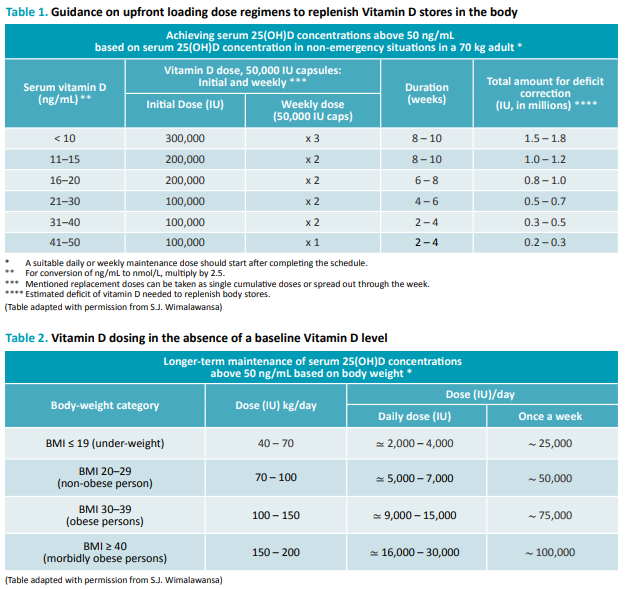
- Vitamin D3: Optimal approach to dosing requires testing of 25(OH)D level. For dosing guidance, see Table 1 if level is known and Table 2 if level is unknown (below) (Amazon)
- Vitamin C: 500 - 1,000 mg BID (twice daily) (Amazon)
- Quercetin: 250 mg daily. (Amazon)
- Zinc: 30 - 40 mg/day (elemental zinc). Zinc lozenges are preferred. (Amazon)
- Melatonin: 6 mg before bedtime (causes drowsiness). (Amazon)
Ivermectin Alternative
- Nigella Sativa 40mg/kg daily (black seed) (Amazon)
To be used if ivermectin not available or added to ivermectin for optimal prevention.
Notes:
- High risk Individuals: > 60 years with co-morbidities (hypertension, diabetes, chronic lung disease, chronic kidney disease), obesity, long term care facilities, etc.
- Post COVID-19 exposure: To use if a household member is COVID-19 positive, or you have prolonged exposure to a COVID-19 positive patient without wearing a mask.
- Precautionary Note: Ivermectin has a number of potentially serious drug-drug interactions. Please check for potential drug interaction at Ivermectin Drug Interactions - Drugs.com. The most important drug interactions occur with cyclosporin, tacrolimus, anti-retroviral drugs, and certain anti-fungal drugs.
- Due to the possible drug interaction between quercetin and ivermectin (may increase ivermectin levels), these drugs should not be taken simultaneously (i.e. should be staggered morning and night).
- Ivermectin is also lipophilic and therefore, bioavailability is maximised on a full stomach; or best to be taken with meal.
- Vitamin D3 RDA (Recommended Daily Allowance) is 800–1000 IU/day. The safe upper-dose daily limit is likely < 4000 IU/day. Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with an increased risk of acquiring COVID-19 and from dying from the disease. Vitamin D supplementation may therefore prove to be an effective and cheap intervention to lessen the impact of this disease, particularly in vulnerable populations, i.e. the elderly and obese.
- When Is the Best Time to Take Vitamin D? Morning or Night? It is possible that increasing vitamin D levels during the day may act, in part, as a signal that suppresses melatonin generation (source). Therefore, it's better to take vitamin D (with meal) during the day and melatonin to be taken just before bedtime.
- It is likely that vitamin C and quercetin have synergistic prophylactic benefit. Quercetin should be used with caution in patients with hypothyroidism and TSH levels should be monitored.
- Please consult with a qualified doctor and only use human ivermectin. Ivermectin for animals contain excipients (binding and storage compounds such as polyethylene glycol (PEG)) that are known to cause liver failure in high doses.
- There have been reports of visual problems associated with ivermectin. However, the effect is minor and transient.
Related:
EARLY TREATMENT PROTOCOL
For early outpatient protocol (COVID-19 positive), the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Working Group, FLCCC I-MASK+ protocol recommends:
1. First line agents (use any or all medicines; listed in order of priority/importance)
Anti-Virals
- Ivermectin: 0.4–0.6 mg/kg per dose (take with or after meals) — one dose daily, take for 5 days or until recovered. (Find a Doctor). Use upper dose range if: 1) in regions with more aggressive variants (e.g. Delta); 2) treatment started on or after day 5 of symptoms or in pulmonary phase; or 3) multiple comorbidities/risk factors. (Ref)
- Hydroxychloroquine (preferred for Omicron): 200mg PO twice daily; take for 5 days or until recovered. (Find a Doctor)
Anti-Septic Anti-virals
- Antiviral mouthwash: Gargle 3 x daily (do not swallow; must contain chlorhexidine, povidone-iodine, or cetylpyridinium chloride). (e.g. Crest mouthwash, Scope mouthwash™, Colgate mouthwash, Betadine® Antiseptic Sore Throat Gargle)
- Iodine Nasal Spray/Drops: Use 1 % povidone iodine commercial product as per instructions 2–3 x daily. If 1 %-product not available, must first dilute the more widely available 10 %-solution and apply 4–5 drops to each nose every 4 hours. (No more than 5 days in pregnancy)
Anti-Coagulants + Immune Fortifying
- Aspirin: 325 mg/day unless contraindicated. (Amazon)
- Vitamin D3: Optimal approach to dosing requires testing of 25(OH)D level. For dosing guidance, see Table 1 if level is known and Table 2 if level is unknown (above) (Amazon)
- Melatonin: 10 mg before bedtime (causes drowsiness). (Amazon)
Synergistic Therapies
- Vitamin C: 500 - 1,000 mg BID (twice daily) (Amazon)
- Quercetin: 250 mg twice a day. (Amazon)
- Zinc: 100 mg/day. Zinc lozenges are preferred. (Amazon)
Nutritional Therapeutics (New)
Pulse Oximeter
FLCCC also recommend monitoring your oxygen saturation with a pulse oximeter and to go to the hospital if you get below 94%. (Amazon)
Other Alternatives:
- Optional: Betadine nasal spray applied 3 times a day (Ref) (Amazon)
- Optional: Xlear Nasal Spray with Xylitol: use twice a day (Ref) (Amazon)
- Optional: Azithromycin 250 mg twice a day. (Ref) (Find a Doctor).
- Optional: Bromhexine 8 mg three times a day (Ref) (Lazada Malaysia*)
* Not available on Amazon
2. Second line agents (listed in order of priority /importance)
Add to first line therapies above if:
1) ≥5 days of symptoms;
2) Poor response to therapies above;
3) Significant comorbidities
- Spironolactone 100 mg 2 x daily for ten days
- Dutasteride 2 mg on day 1, followed by 1 mg daily for 10 days. If dutasteride is not available, use finasteride 10 mg daily for 10 days.
Fluvoxamine
Consider fluoxetine (Prozac) 30mg daily for 10 days as an alternative (it is often better tolerated).
Avoid if patient is already on an SSRI.
Notes:
- Combining fluvoxamine and melatonin may significantly increase the blood levels and effects of melatonin (Drugs.com). You can check for other potential drug interactions with fluvoxamine at Fluvoxamine Drug Interactions - Drugs.com.
- Some individuals who are prescribed fluvoxamine experience acute anxiety which needs to be carefully monitored for and treated by the prescribing clinician to prevent rare escalation to suicidal or violent behavior.
Monoclonal antibody therapy
Sotrovimab: 500mg each in a single intravenous infusion. Antibody therapy is for patients within 5 days of first symptoms, non-severe symptoms, and one or more risk factors as:
- Age>55y;
- BMI>25;
- pregnancy;
- chronic lung, heart, or kidney disease;
- diabetes.
Trials data supporting sotrovimab against Omicron are not available, however the manufacturer has claimed it retains neutralizing capability against this variant.
3. Third line agent
To consider if after day 7–10 from first symptoms and patient has either: abnormal chest x-ray, shortness of breath, or oxygen saturations of 88–94%. If oxygen saturation is lower than 88%, emergency room evaluation should be sought.
Prednisone or Methylprednisolone: 1mg/kg daily for 5 days followed by slow taper or escalation according to patient response.
Behavioral Prevention
- Face Masks - Must wear cloth, surgical, or N95 mask (without valve) in all indoor spaces with non-household persons. Must wear a N95 mask (without valve) during prolonged exposure to non-household persons in any confined, poorly ventilated area.
- Social Distancing - Until the end of the COVID-19 crisis, we recommend keeping a minimum distance of approx. 2 m / 6 feet in public from people who are not from your own household.
- Wash Hands - We recommend, after a stay during and after outings from home (shopping, sub - way etc.), a thorough hand cleaning (20–30 sec. with soap), or also to use a hand disinfectant in between.
For an up-to-date overview of all published studies on ivermectin in the treatment and prevention of COVID-19 we recommend visiting C19Early.
For post-COVID or long COVID syndrome, check out Long Haulers Treatment Protocol. For a simplified version of the I-MASK+ protocol, the FLCCC has also developed the I-MASS protocol.
Other Early treatment options (Editor's edition)
We've have added a few more options and alternatives that the FLCCC I-MASK protocol has yet to include, such as:
- Paxlovid from Pfizer (Find a Doctor).
- Budesonide 1mg/2cc solution via nebulizer twice a day for 7 days (not suitable during viral phase)
- Nasal Spray: Xlear Nasal Spray with Xylitol (Ref) (Amazon)
- Aspirin: 325 mg/day unless contraindicated. (Amazon) (not suitable during viral phase)
- NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine) 500 mg twice a day.
- Bromhexine 8 mg three times a day (Ref) (Lazada Malaysia*)
* Not available on Amazon





.png)

Comments
Post a Comment