LeBron James’ Eldest Son’s Sudden Cardiac Arrest, Physician Recommends 4 Heart-Healthy Foods
Bronny James, the 18-year-old son of NBA Lakers star LeBron James, experienced a sudden cardiac arrest during basketball training at the University of Southern California on July 25, 2023 and was immediately taken to the hospital. He was discharged three days later and is currently recovering at home.
In June 2023, Oscar Cabrera Adames, a Dominican professional basketball player, tragically died at the young age of 28 due to heart disease. He claimed to have developed myocarditis after receiving two doses of the vaccine.
There was a significant increase in myocarditis cases following the initial rollout of COVID-19 vaccines two years ago. A large-scale statistical study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) in 2021 involving over 2 million people found that before vaccination (2019 to 2021), the mean number of myocarditis or myopericarditis cases per month was approximately 16.9, while during the vaccination period (February to May 2021), the mean number of cases increased to 27.3 per month.
Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle, while pericarditis is inflammation of the fibrous tissue surrounding the heart. The study also revealed that younger individuals are more likely to experience myocarditis after vaccination, whereas pericarditis is more prevalent than myocarditis among older individuals.
In July 2023, Canadian researchers published a systematic review in the BMJ Open, an affiliated journal of the British Medical Journal (BMJ). The study revealed that while the observed number of myocarditis or pericarditis cases was not significant, individuals who received mRNA COVID-19 vaccines had a twofold higher risk of developing myocarditis or pericarditis compared to those who were not vaccinated in the absence of COVID-19 infection.
A study published in 2022 in the journal Nature Reviews Cardiology, an affiliated journal of the prestigious journal Nature, revealed that the highest incidence of myocarditis happened after the second dose of the vaccine, and the majority of cases occurred in young men. Additionally, most cases were reported within three to four days after vaccination.
The authors suggest that the occurrence of myocarditis in individuals after receiving mRNA vaccines is rare, and it usually resolves within a few days or weeks. They believe that the benefits of vaccination outweigh the risks and, therefore, recommend adolescents and adults to receive COVID-19 vaccines.
Caution Against Vigorous Exercise After Heart Inflammation
On the NTDTV program “Health 1+1,” Dr. Yuhong Dong, a virologist and infectious disease specialist in Europe, pointed out that the incidence of myocarditis and pericarditis demonstrates a linear upward trend after vaccination. Dr. Dong believes that vaccination cannot completely prevent the spread of the virus, as gene expression, overall health conditions, and immune strength vary among individuals. Therefore, vaccination does not guarantee immunity, and not getting vaccinated does not necessarily lead to infection.
In the program, Dr. Dong also shared four recovery tips for patients with heart inflammation.
- Rest and avoid strenuous exercise and heavy physical labor for the next six months, refraining from activities that put a strain on the heart.
- Be mindful of your diet and avoid consuming stimulants that can affect the heart, like beverages containing caffeine.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, balance work and rest, avoid staying up late, and manage emotions.
- Follow hospital treatment and engage in both physical and mental exercises to support full recovery of the heart.
4 Heart-Healthy Foods Experts Recommend
On the NTDTV program “Health 1+1,” Jonathan Liu, a Chinese medicine professor at Georgian College in Canada, recommended four heart-healthy foods:
- Carrots are rich in carotenoids and vitamin A, which not only strengthen eyesight but also support the health of epithelial tissues, enhance immune function, protect various organs, and clear free radicals. Studies have found that individuals who consume more carotenoids have a lower risk of developing various cardiovascular diseases.
- Blueberries contain anthocyanins, which can prevent oxidative reactions, thus protecting heart and vascular health. They also contain anti-inflammatory compounds that can reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Black fungus is known for its ability to reduce blood viscosity, which helps prevent blood clots.
- Tomatoes are rich in lycopene, a natural antioxidant that neutralizes harmful free radicals and helps prevent the worsening of heart inflammation. A study (pdf) indicated that having a high concentration of lycopene in the blood can lower the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Related Studies
Several other prospective studies examine myocarditis following Pfizer vaccination.In Taiwan, researchers established baseline electrocardiogram levels before a second Pfizer dose and recorded abnormal results following the administration in one percent of 4,928 primary school students. That included five students diagnosed with myocarditis or an abnormal heartbeat.
In Israel, a study of 324 health care workers with a median age of 51 who received a second Pfizer booster identified two cases of vaccine-induced heart injury on day three.
Other recent studies have confirmed that vaccine-induced myocarditis can kill, including a South Korean study that ruled out all other possible causes for eight sudden deaths following messenger RNA vaccination. Myocarditis was not suspected as a clinical diagnosis or cause of death before autopsies were performed, researchers said.The Incidence of Myocarditis and Pericarditis in Post COVID-19 Unvaccinated Patients - A Large Population-Based Study
However, a retrospective cohort study of 196,992 adults after COVID-19 infection in Israel between March 2020 and January 2021 concluded that "We did not observe an increased incidence of neither pericarditis nor myocarditis in adult patients recovering from COVID-19 infection." (J Clin Med 2022)
A study out of Massachusetts by Yonker and colleagues explored the significance of vaccine-induced spike protein. The researchers collected blood from 16 adolescent and young adult patients hospitalized with postvaccine myocarditis. They used these blood samples to compare the patients’ immune profiles to those of 45 healthy, age-matched control patients who had also received the vaccine. Three quarters of the myocarditis patients had developed the pathology after the second dose. The researchers did not include a control group of unvaccinated individuals.
SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Myocarditis in a Nordic Cohort Study of 23 Million Residents (JAMA)
In a cohort study (JAMA 2022) of 23.1 million residents across 4 Nordic countries, risk of myocarditis after the first and second doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines was highest in young males aged 16 to 24 years after the second dose.
The study concluded that the risk of myocarditis was highest in young males after the second SARS-CoV-2 vaccine dose, and this risk should be balanced against the benefits of protecting against severe COVID-19 disease.
Got the Jab? Take Action to Safeguard Your Health
At present, the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC) seems to have one of the best treatment protocols for post-jab injuries. It’s called I-RECOVER and can be downloaded from covid19criticalcare.com.
The World Health Council has also published lists of remedies that can help inhibit, neutralize and eliminate spike protein, which most experts agree is the primary culprit. See, “World Council for Health Reveals Spike Protein Detox.”
Other Helpful Treatments and Remedies
Other treatments and remedies that may be helpful for COVID jab injuries include:• Lower your omega-6 intake. Linoleic acid is consumed in amounts 10 times higher than the ideal in well over 95% of the population and contributes to massive oxidative stress that impairs your immune response. Seed oils and processed foods need to be diligently avoided. See “Linoleic Acid — The Most Destructive Ingredient in Your Diet” for more information.
• Pharmaceutical grade methylene blue, which improves mitochondrial respiration and assists in mitochondrial repair. A dose of 15 to 80 milligrams a day could go a long way toward resolving some of the fatigue many suffer post-jab.
It may also be helpful in acute strokes. The primary contraindication is if you have a G6PD deficiency (a hereditary genetic condition), in which case you should not use methylene blue at all. To learn more, see “Health Benefits of Methylene Blue.”
• Lumbrokinase, nattokinase and serrapeptidase are fibrinolytic enzymes that, when taken on an empty stomach one hour before a meal, or two hours after, will help reduce your risk of blood clots. See "Lumbrokinase vs nattokinase vs serrapeptidase".


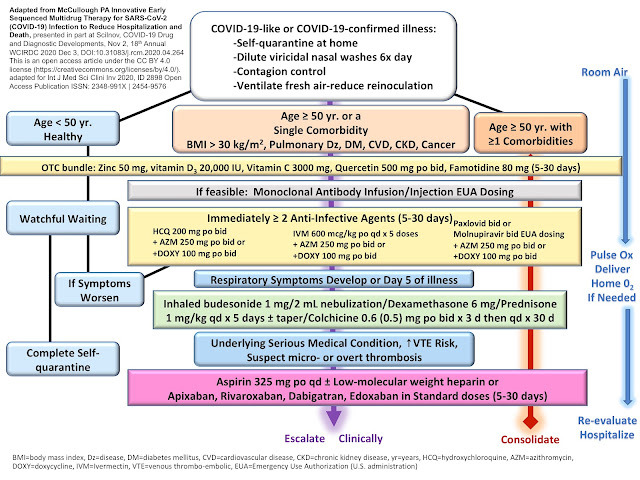



.png)

Comments
Post a Comment